Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 14
Reviewed
Eight-spotted forester caterpillars (Alypia octomaculata) are present from spring to early fall. They produce one to two generations per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 49
Reviewed
Variegated fritillary caterpillars (Euptoieta claudia) are present from June to October. They produce multiple generations per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 17
Reviewed
Fall webworm caterpillars (Hyphantria cunea) are present from spring to fall. They produce two to three generations per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 52
Reviewed
Whitelined sphinx caterpillars (Hyles lineata) are present from spring to early fall. They produce one to two generations per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden
Reviewed
Caterpillars are some of the most easily observed insects in backyards and gardens. Learn to identify them so you will know what type of butterflies or moths they will turn into.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 20
Reviewed
Green cloverworm caterpillars (Hypena scabra) are present from summer to fall. They produce three generations per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 55
Reviewed
Yellownecked caterpillars (Datana ministra) are present from July to September. They produce one generation per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 23
Reviewed
Hag moths caterpillars (Phobetron pithecium) are present in summer and fall. They produce one generation per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 26
Reviewed
Imported cabbageworm caterpillars (Pieris rapae) are present from early spring to summer. They produce multiple generations per year.
Reducing Losses When Feeding Hay to Beef Cattle
Reviewed
Feeding hay to cattle is expensive, mostly due to waste. Learn good management practices to minimize the losses that occur due to poor storage methods, improper feeding methods, or both.
Missouri Farm Labor Guide
Revised
Learn good human resource practices related to employee recruitment, hiring, onboarding, training and termination that your farm or agribusiness can use.
Pelvic Measurements and Calving Difficulty
Reviewed
Although researchers agree that birth weight is the most important measurable trait affecting calving difficulty, there is evidence that the size and shape of the pelvis also affect a heifer’s ability to calve.
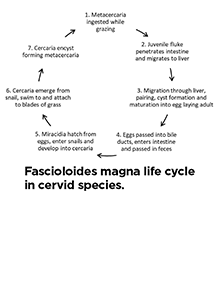
Liver Flukes in Missouri: Distribution, Impact on Cattle, Control and Treatment
Reviewed
Cattle operations should evaluate their risk for is Fascioloides magna, also known as the deer fluke or the giant liver fluke. Learn about its distribution in Missouri, its life cycle, treatment and more in this guide.
Enlist Label Compliance: How to Determine Hydrologic Soil Groups
New
Learn how to use the USDA Web Soil Survey interactive map to determine your field's hydrologic soil group for the soil series on which you plan to apply an Enlist herbicide.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 25
Reviewed
Huckleberries are stiffly branched leafy shrubs or small trees, often found in extensive colonies, from 6 inches to 10 feet tall. The alternate, simple leaves are 3/4 to 3 inches long and 1/2 to 1 inch wide. The fruits are blue to black berries with a faint whitish coating.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 57
Reviewed
Three species of wild bean occur in the Midwest. Each is a somewhat small plant with twining vines and relatively small leaves composed of three leaflets. Seeds are present in hairy pods.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 28
Reviewed
Jewelweed commonly reaches 18-24 inches. Leaves have scalloped edges and fleshy stems that exude a clear, watery gel-like liquid when crushed. Flowers are orange (I. capensis) or pale yellow (I. pallida).
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 31
Reviewed
Little bluestem is a native grass that occurs in clumps with fine leaves less than 1/4 inch wide. Seed stalks are commonly 2 to 3 feet tall. Stems are hairy and flattened near the base. Seeds are light and fluffy.
Developing Effective Communications
Reviewed
Most Americans probably do not appreciate the importance of communication in their personal and workday lives. Hopefully, those of us in extension work recognize the importance of good, effective communications.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 34
Reviewed
Orchard grass is a cool-season bunch grass. Its leaves have a bluish cast. Close inspection of the leaf collar reveals a flattened shape and membranous ligule. Its rather distinctive seed heads form by late May. Height at maturity averages 3 feet.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 02
Reviewed
Refer to this glossary for definitions of words and phrases related to plants.
Writing Columns
Reviewed
Before writing a column, think about purpose, audience, content and structure. Visit our website today to learn more about writing columns.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 37
Reviewed
Partridge pea grows from 12 to 18 inches up to 3 feet tall. It has compound, alternate leaves. Leaflets are less than 1 inch long. Flowers are bright yellow with reddish-purple bases, about 1 inch across. Ripened seedpods are red-brown.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 05
Reviewed
Barnyardgrass is most often found growing in moist areas. The large seeds of this grass make it an important food source for bobwhites.