Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 22
Reviewed
Hackberry emperor caterpillars (Asterocampa celtis) are present from early summer to fall. They produce two generations per year.
Safe Drinking Water in an Emergency
Reviewed
You and your family can survive for several days without food, but only a short time without water. Disasters can often cause us to question the safety of our drinking water. With a little planning and preparation, you can be prepared by having a safe emergency water supply.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 25
Reviewed
Imperial moth caterpillars (Eacles imperialis) are present from June to August. They produce two generations per year. Common host plants include oaks, sweetgum, maple, hickory, sassafras, elm and sycamore.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 28
Reviewed
Linden looper caterpillars (Erannis tiliaria) are present from late spring to summer. They produce one generation per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 31
Reviewed
Pale tussock moth caterpillars (Halysidota tessellaris) are present from early summer to fall. They produce two generations per year.
Checking and Disinfecting Flooded Wells
Reviewed
If your well has been flooded, the well and entire water system should be cleaned and disinfected. Floods can contaminate wells with silt, raw sewage, oil and disease organisms.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 34
Reviewed
Polyphemus moth caterpillars (Antheraea polyphemus) are present from May to October. They produce multiple generations per year.
Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 02
Reviewed
Achemon sphinx caterpillars (Eumorpha achemon) are present from early summer to fall. They produce one to two generations per year.
Reducing Losses When Feeding Hay to Beef Cattle
Reviewed
Feeding hay to cattle is expensive, mostly due to waste. Learn good management practices to minimize the losses that occur due to poor storage methods, improper feeding methods, or both.
Enlist Label Compliance: How to Determine Hydrologic Soil Groups
New
Learn how to use the USDA Web Soil Survey interactive map to determine your field's hydrologic soil group for the soil series on which you plan to apply an Enlist herbicide.
Missouri Farm Labor Guide
Revised
Learn good human resource practices related to employee recruitment, hiring, onboarding, training and termination that your farm or agribusiness can use.
Pelvic Measurements and Calving Difficulty
Reviewed
Although researchers agree that birth weight is the most important measurable trait affecting calving difficulty, there is evidence that the size and shape of the pelvis also affect a heifer’s ability to calve.
Liver Flukes in Missouri: Distribution, Impact on Cattle, Control and Treatment
Reviewed
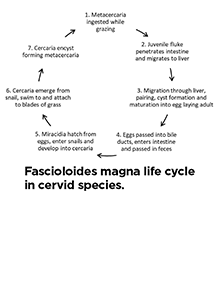
Cattle operations should evaluate their risk for is Fascioloides magna, also known as the deer fluke or the giant liver fluke. Learn about its distribution in Missouri, its life cycle, treatment and more in this guide.
Writing Features
Reviewed
Good feature writers are imaginative, curious, nosey, attentive, unconventional, witty, and usually are not above "borrowing" a good writing idea from someone else.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 33
Reviewed
Oaks are long-lived trees that produce a seasonally important food for dozens of wildlife species. Their distinctive leaves and bark are identifying features.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 04
Reviewed
American plum can grow as a small tree up to 20 feet high but more commonly occurs in colonies or thickets by sending up root suckers and shoots.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 36
Reviewed
More than three dozen species of panic grass are commonly found across the Midwest. Seeds are football-shaped and borne on a sprawling, panicle-shaped seed head. The leaves of panic grasses resemble flags along the stem.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 07
Reviewed
Bidens is most often found in moist areas. It has yellow flowers that are 1 to 1.5 inches.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 39
Reviewed
Pigweed leaves are alternate and simple. Small green or tan flowers produce small, round, shiny black seeds. The roots are red when pulled. Depending on the species, pigweed may grow 1 to 8 feet tall.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 10
Reviewed
Broomsedge is a native warm-season grass that is often confused with little bluestem, but broomsedge stems are the more flattened and more densely leafed. Also, broomsedge in the fall/winter is typically yellowish tan, while little bluestem has a bronzy color.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 42
Reviewed
Possum haw grows mostly as a shrub but sometimes as a tree up to 30 feet tall. The twigs are slender with short, spurlike lateral twigs. The white flowers bloom in mid-spring either singularly or in clusters. Fruits are orange to red and globe-shaped.
Controlling Voles in Horticulture Plantings and Orchards in Missouri - Page 3
Reviewed
Meadow voles and prairie voles spend most of their lives above ground, living in and feeding on grasses and seeds. They may travel as far as 1/4 mile in search of food and cover. Their typical habitat includes lightly grazed pastures, old fields and grassy areas, lawns and gardens.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 13
Reviewed
Shrub dogwoods are common in fence lines and along forest edges. Individual plants are rather short (less than 12 feet tall) and somewhat rounded.