Essentials of Fire Fighting, Seventh Edition Manual and Course Workbook Package
New $115
Save when you purchase the Essentials of Fire Fighting, Seventh Edition Manual and Course Workbook Package.
Sunflowers: A Versatile Native Crop
New
Sunflowers are an amazingly versatile crop with a fascinating history. Visit our site to view our Sunflowers: A Versatile Native Crop article.
Establishing Mixtures of Native Warm-Season Grasses and Forbs for Potential Biomass, Forage and Wildlife Habitat
New
Learn about the species of native warm-season grasses with potential for biomass production, livestock forage and wildlife habitat in Missouri — switchgrass, indiangrass, big bluestem, little bluestem and eastern gamagrass — in this MU Extension guide.
Turfgrass Weed Control for Professionals (2020 Edition)
New
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available for purchase from the Purdue Extension Education Store.
Tree Pests: Gypsy Moth
New
Introduction
Gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar) is a destructive, exotic forest pest that was accidentally introduced into the United States in 1869 by a man hoping to mate them with silkworms to create a hardier, more productive silk-bearer.
Tree Pests: Gypsy Moth - Page 4
New
Slow the spread of gypsy moth
Tree Pests: Native Pests - Page 2
New
Oak wilt
Oak wilt is a lethal disease of oaks, especially species in the red oak group. A fungus invades the tree, which causes it to die. In Missouri, the oak wilt fungus is spread primarily when sap-feeding beetles carry oak wilt spores to fresh wounds during the early part of the growing season.
Tree Pests: Native Pests - Page 5
New
Rapid white oak mortality
Beginning in August 2011 and continuing through fall 2013, the Missouri Department of Conservation’s Forest Health staff received many reports of rapid white oak decline and mortality, often occurring within one growing season. In 2013, a majority of reports came from east central and southeast Missouri.
Tree Pests: Gypsy Moth - Page 2
New
Gypsy moths signs and symptoms
Adults vary by sex.
Tree Pests: Gypsy Moth - Page 5
New
Before you report a possible gypsy moth find
Many native, less damaging moths that look similar to gypsy moths, are present in Missouri and do not need to be reported. Consult the gypsy moth signs and symptoms page before reporting. Early detection is useful only when the problem is contained and eradicated.
Tree Pests: Native Pests - Page 3
New
Hypoxylon canker
Hypoxylon canker is a common disease of hardwoods, especially species in the red oak group. It is often one of several factors ultimately responsible for tree death. A disease of the inner bark and sapwood, Hypoxylon damages tissues used by the tree to conduct water from soil to the leaves.
Tree Pests: Gypsy Moth - Page 3
New
Where gypsy moth has been found
Every year, more than 6,000 gypsy moth traps
Tree Pests: Native Pests
New
Introduction
In addition to all of the nonnative, invasive tree pests challenging the health of Missouri’s trees, there are several native insects and diseases that can cause serious harm.
Tree Pests: Native Pests - Page 4
New
Oak decline
Trees are weakened by environmental stresses such as drought, waterlogging, frost or by pests such as defoliating or sucking insects. Weakened trees are then invaded and killed by insects and diseases that cannot successfully attack healthy trees. Usually the progression of decline is slow, and it occurs over several years.
Tree Pests: Thousand Cankers Disease - Page 3
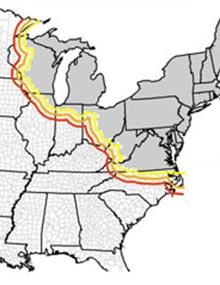
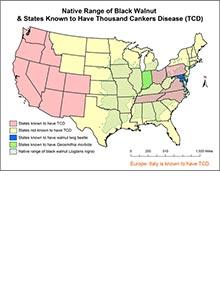
New
Where TCD has been found
Thousand cankers disease occurs in nine western and five eastern states (shaded pink); the year in which the disease was confirmed is noted. Since 2010, TCD has been confirmed in Ohio, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Tennessee and Virginia.
Tree Pests: Thousand Cankers Disease - Page 6
New
Slow the spread of TCD
You can help minimize the chances of spreading TCD by following these steps:
Tree Pests: Asian Longhorned Beetle
New
Introduction
The invasive Asian longhorned beetle (ALB) hitchhiked to the United States nestled deep within hardwoods cut into crates and pallets and used to import goods from Asian countries.
Tree Pests: Asian Longhorned Beetle - Page 4
New
ALB quarantine information
Currently, there are no interior or exterior ALB quarantines for the state of Missouri.
Tree Pests: Thousand Cankers Disease - Page 4
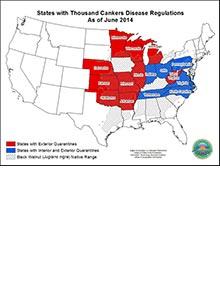
New
TCD quarantine information
TCD is not federally regulated, but be aware that individual states have enacted state-level or county-level quarantines restricting the movement of untreated walnut materials of all kinds.
Tree Pests: Thousand Cankers Disease - Page 7
New
Before you report a possible TCD find
To determine if you should report TCD, ask yourself these questions:
Is my tree a walnut tree?
Determine if your tree is a walnut. If the answer to this question is yes, move to the next question.
Tree Pests: Asian Longhorned Beetle - Page 2
New
ALB signs and symptoms Signs
Adult Asian longhorned beetles (Anopl
Tree Pests: Asian Longhorned Beetle - Page 5
New
Slow the spread of ALB
We must remain vigilant so we can eradicate any infestations should they occur. Transporting firewood or other wood materials from an infested area can spread ALB. So, the same common sense practices for slowing the spread of emerald ash borer and thousand cankers disease apply to ALB, namely:
Tree Pests: Thousand Cankers Disease
New
Introduction
Although not yet detected here, thousand cankers disease (TCD) is a potentially fatal disease of black walnut, caused by the walnut twig beetle (Pityophthorus juglandis) and an associated fungus (Geosmithia morbida).
Tree Pests: Thousand Cankers Disease - Page 5
New
TCD management
Controls for TCD have not yet been identified and their development will require better understanding of the biology of the walnut twig beetle and the canker-producing fungus. Because of the extended period when adult beetles are active, insecticide spray applications will likely have limited effectiveness.