Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 47
Reviewed
Sideoats grama has fine leaves and widely spaced fine hairs along the leaf edge, especially near the collar. Most sideoats plants are 18-24 inches tall at maturity. It has a unique, oatlike seed that droops slightly off one side of the stalk.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 15
Reviewed
Common elderberry is a shrub that grows to 8 feet tall and forms dense colonies from root sprouts. The tops are multibranched, bearing opposite, pinnately compound leaves 4 to 12 inches long. Lance-shaped leaflets are 2 to 6 inches long, 1 to 2 inches wide and sharply toothed.
Managing for White-tailed Deer in Missouri: Setting and Accomplishing Management Goals
Reviewed
White-tailed deer management
This deer conservation guide is one in a series developed jointly by MU Extension and the Missouri Department of Conservation.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 50
Reviewed
Winged, smooth and staghorn sumac have single stems and a broad reaching canopy of pinnately compound leaves. Fragrant sumac has three leaves resembling poison ivy but with more serrated margins. The leaves of all species often turn a brilliant red in autumn.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 18
Reviewed
Most of the foxtails found in the Midwest are native to Europe and Asia. They are annual plants generally considered to be weeds. The seed head has the bushy form of a fox's tail. Height at maturity varies by species, but is generally 1-3 feet.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 53
Reviewed
Three-seeded mercury is characterized by longitudinally folded, lobed, leaflike bracts that persist throughout the growing season. The seeds are small, egg-shaped and dark brown to light gray or tan.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 21
Reviewed
Wild grapes are vines capable of climbing to 75 feet or more by means of tendrils. Leaves are alternate, simple and heart-shaped (Vitis) to triangular (Ampelopsis). Flowers bloom from mid to late spring, and globe-shaped fruits are borne in drooping clusters from late summer through fall.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 56
Reviewed
Viburnum grows as shrubs or small trees with branching crowns. Flowers are borne in dense, flat-topped panicles that produce many red to bluish black, berrylike fruits in fall. The leaves are opposite and turn brilliant shades of deep rose-purple to rose-red or bright red in fall.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 24
Reviewed
Hazelnut is a thicket-forming, spreading shrub that can vary in height from 3 to 10 feet. Its leaves are egg-shaped to oval, doubly serrated with five to eight veins on each side of the central vein. Fruits occur in clusters of two to six.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 59
Reviewed
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the following individuals and groups for their constructive review of this publication: Steve Clubine, Elsa Gallagher, Emily Horner, Lee Hughes, Aaron Jeffries, Matt Seek, Tim Smith, Bill White, and members of the Missouri Quail and Grassland Bird Technical Committee.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 27
Reviewed
Indian grass is a tall, warm-season nativethat averages 4 to 6 feet in height at maturity. Stems are stiff, and leaves are long and narrow. A characteristic of the plant is the notched ligule, suggesting the rear sight of a rifle.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 30
Reviewed
Annual lespedeza and Korean lespedeza exhibit many similarities in growth form, occurring as semierect herbaceous plants with three-lobed leaves and reddish-purple to white flowers. Lower leaves are spreading while upper leaves stand erect.
Fertilizer Nutrients in Dairy Manure
Reviewed
Many dairy producers fall into one of two categories:
Soybean Rust, Page 2
Revised
Bacterial pustule (Xanthomonas axonopodia pv. glycines)
Benefits and Risks of Biosolids
Reviewed
Biosolids are domestic wastewater sludge that meet standards for beneficial use as fertilizer. Visit our site to learn the Benefits and Risks of Biosolids.
Soybean Rust, Page 5
Revised
Septoria brown spot (Septoria glycines)
Soybean Rust, Page 8
Revised
Compare soybean rust disease stages by looking at them side by side.
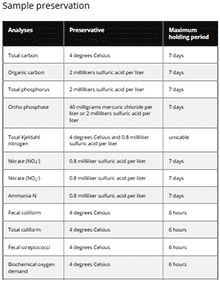
Collecting and Preserving Waste and Wastewater Samples for Analysis
Reviewed
Waste handling systems are used to protect the environment. Visit our site for our Collecting and Preserving Waste and Wastewater Samples for Analysis guide.
Soybean Rust, Page 3
Revised
Downy mildew (Peronospora manshurica)
Soybean Rust, Page 6
Revised
Soybean rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi)
Soybean Rust
Reviewed
Asian soybean rust is a serious foliage disease that has the potential to cause significant soybean yield losses. Anyone involved in soybean production needs to be familiar with the disease and its identification and management.