

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Sign — We Stock Healthy (front door sign or window cling; 4 x 6 inches) (Spanish)
Revised
Retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program can use this 4-by-6-inch Spanish sign or window cling (or English version) to let customers know they are stocking more healthy foods. Learn about this healthy community program.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Sign — We Stock Healthy (small: 8.5 x 11 inches) (Spanish)
Revised
Retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program can use this 8.5-by-11-inch Spanish sign (or English version) to let customers know they are stocking more healthy foods. Learn about this program that aims to create healthy communities.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Loyalty Card — Milk (Spanish)
Revised
Reward customers for buying skim or 1% milk. This Spanish loyalty card, which encourages healthy food purchases, was created for small food-retailers in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program. Also available in English. Print, cut, distribute, punch.

Seasonal Apiary Management for Missouri
Revised
Learn how to establish, manage and maintain beehives to foster healthy bees and produce surplus honey to use or sell. Flowering periods for Missouri honey plants are included in this University of Missouri Extension guide.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Shelf Talkers (Spanish)
Revised
Small food-retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program, help your Spanish-speaking customers make the healthier choice by posting these shelf talkers to present health information about various products. Download, print and hang!

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Recipe Cards (Spanish)
New
These recipe cards are for stores participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program to share with their Spanish-speaking customers to encourage healthy eating.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Sign — We Stock Healthy (large: 24 x 36 inches) (Spanish)
Revised
Retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program can use this 24-by-36-inch Spanish sign (or English version) to let customers know they are stocking more healthy foods. Learn about this program that aims to create healthy communities.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Loyalty Card — Fresh Produce (Spanish)
Revised
Reward customers for buying fresh produce. This Spanish loyalty card, which encourages healthy food purchases, was created for small food-retailers in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program. Also available in English. Print, cut, distribute, punch.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Loyalty Program Sign — Milk (Spanish)
Revised
Encourage customers to buy skim or 1% milk by offering a loyalty program that offers a free half gallon after the purchase of 10. Post this Spanish sign to promote the program. Also available in English. Learn more about Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy today.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Sign — Fruits and Veggies in Cooler (half page) (Spanish)
Revised
Retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program can use this 8.5-by-5.5-inch Spanish sign (or English version) to alert customers to the presence of fruits and vegetables in a cooler. Learn about this healthy community program.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Sign — We Stock Healthy (medium: 11 x 17 inches) (Spanish)
Revised
Retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program can use this 11-by-17-inch Spanish sign (or English version) to let customers know they are stocking more healthy foods. Learn about this program that aims to create healthy communities.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Loyalty Program Sign — Fresh Produce (Spanish)
Revised
Encourage customers to buy fresh produce by offering a loyalty program that offers a free fresh item after the purchase of 10. Post this Spanish sign to promote the program. Also available in English. Learn more about Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy today.
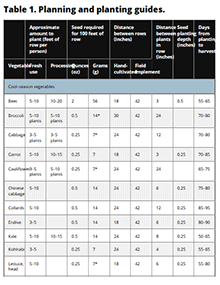
Vegetable Planting Calendar, Page 2
Reviewed
Discover the vegetable planting calendar with helpful guides for planting dates, seed requirements, and row spacing for both cool and warm-season vegetables.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Table Tent — Free Tastes (Spanish)
Revised
Small food-retailers, stock healthy so your customers can shop healthy. Use this table tent to encourage your Spanish-speaking customers to sample a healthy food you are promoting as part of the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program.
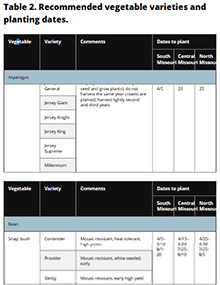
Vegetable Planting Calendar, Page 3
Reviewed
Table 2 lists recommended vegetable varieties and planting dates.

Vegetable Planting Calendar
Reviewed
Plant a vegetable garden to save on your family food bill and promote good dietary habits. The tables in this guide help Missourians plan what to plant, when to plant and how much of each vegetable to plant.

Establishment and Care of Woody Ornamentals
Reviewed $10
Learn to select, plant, and care for trees and shrubs suited to your landscape, ensuring health and resilience in varying conditions.
Plans Examiner Blueprints
New $39.60
These blueprints are designed to support the information in the Plans Examiner for Fire and Emergency Services, Second Edition Manual. They are referenced in various locations throughout the manual and intended to provide the student with an example of what they will encounter when performing the tasks of a plans examiner.

Fire Department Incident Safety Officer, Third Edition Manual
New $110
This manual prepares aspiring and current incident safety officers (ISOs) to meet and exceed the specific job requirements outlined in Chapter 5 of NFPA 1521: Standard for Fire Department Safety Officer Professional Qualifications, 2020 Edition.

Plans Examiner for Fire and Emergency Services, Second Edition Manual
New $58.91 to $69.30
This manual is for fire department staff and others who review plans for compliance with fire and building codes to ensure public safety in the built environment. Its content is appropriate for any plan examiners in fire prevention divisions, fire marshal bureaus, building departments and community risk reduction organizations.

Tree and Shrub Pests Around the Home: Symptoms, Signs and Control
Revised $10
Learn to identify common insect and mite infestation on nearly 100 trees and shrubs and their potential treatments with the help of the University of Missouri Extension publication.

Plans Examiner for Fire and Emergency Services, Second Edition Manual and Blueprints Package
New $86.27 to $95
This manual is for fire department staff and others who review plans for compliance with fire and building codes to ensure public safety in the built environment. The blueprints are referenced in various locations throughout the manual and intended to provide the student with an example of what they will encounter when performing the tasks of a plans examiner.

Fire Protection, Detection, and Suppression Systems, Fifth Edition Manual
New $75.74 to $89.10
The purpose of this manual is to familiarize fire service members and other interested personnel with the components, design, maintenance, operation, testing and inspection of common fire protection, detection and suppression systems. The scope of this manual is to provide up-to-date information on fire protection, detection and suppression systems.

Exercising in the Heat
Reviewed
Exercising in hot conditions can lead to heat-related illnesses like cramps, exhaustion, or stroke. Learn how to stay safe and recognize warning signs.

Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy: Sign — Deli: Apple for Dessert (Spanish)
New
Retailers participating in the Stock Healthy, Shop Healthy program can use this 8.5-by-5.5-inch sign to encourage Spanish-speaking deli customers to have an apple for dessert. Learn about this program that aims to create healthy communities.