

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 09
Reviewed
Cecropia moth caterpillars (Hyalophora cecropia) are present from May to August. They produce one generation per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 41
Reviewed
Spiny oak slug caterpillars (Euclea delphinii) are present in summer and fall. They produce one to two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 12
Reviewed
Dusty birch sawfly caterpillars (Croesus latitarsus) are present in summer and fall. They produce two to three generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 44
Reviewed
Tiger swallowtail caterpillars (Papilio glaucus) are present from May to October. They produce two to three generations per year. Preferred host plants include hoptree, birch, tulip tree, ash, basswood, cherry, apple, willow and magnolia.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 15
Reviewed
Elm sawfly caterpillars (Cimbex americana) are present from summer to fall. They produce one generation per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 47
Reviewed
Unicorn caterpillars (Schizura unicornis) are present from summer to fall. They produce one generation per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 18
Reviewed
Garden webworm caterpillars (Achyra rantalis) are present from late spring to fall. They produce two to three generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 50
Reviewed
Viceroy caterpillars (Limenitis archippus) are present from early summer to fall. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 21
Reviewed
Greenstriped mapleworm caterpillars (Dryocampa rubicunda) are present from late spring to late fall. They produce one to two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 53
Reviewed
Whitemarked tussock moth caterpillars (Orgyia leucostigma) are present from May to October. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 24
Reviewed
Hickory horned devil caterpillars (Citheronia regalis) are present from July to October. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 56
Reviewed
Zebra swallowtail caterpillars (Graphium marcellus) are present from May to November. They produce two to three generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 27
Reviewed
Io moth caterpillars (Automeris io) are present from July to October. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden
Reviewed
Caterpillars are some of the most easily observed insects in backyards and gardens. Learn to identify them so you will know what type of butterflies or moths they will turn into.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 30
Reviewed
Orangedog caterpillars (Papilio cresphontes) are present from July to October. They produce two generations per year. They are considered a pest to citrus trees.

Reducing Losses When Feeding Hay to Beef Cattle
Reviewed
Feeding hay to cattle is expensive, mostly due to waste. Learn good management practices to minimize the losses that occur due to poor storage methods, improper feeding methods, or both.

Pelvic Measurements and Calving Difficulty
Reviewed
Learn how pelvic measurements can help estimate calf birth weight and reduce calving difficulty in beef cattle.

Enlist Label Compliance: How to Determine Hydrologic Soil Groups
New
Learn how to use the USDA Web Soil Survey interactive map to determine your field's hydrologic soil group for the soil series on which you plan to apply an Enlist herbicide.
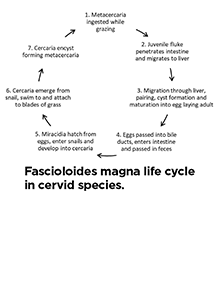
Liver Flukes in Missouri: Distribution, Impact on Cattle, Control and Treatment
Reviewed
Cattle operations should evaluate their risk for is Fascioloides magna, also known as the deer fluke or the giant liver fluke. Learn about its distribution in Missouri, its life cycle, treatment and more in this guide.
Decision-Making Techniques for Community Groups
Reviewed
Explore four decision-making techniques to help community groups identify and prioritize projects effectively.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 05
Reviewed
Barnyardgrass is most often found growing in moist areas. The large seeds of this grass make it an important food source for bobwhites.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 37
Reviewed
Partridge pea grows from 12 to 18 inches up to 3 feet tall. It has compound, alternate leaves. Leaflets are less than 1 inch long. Flowers are bright yellow with reddish-purple bases, about 1 inch across. Ripened seedpods are red-brown.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 08
Reviewed
Mature seed stalks of big bluestem are copper colored and often grow more than 5 feet tall. The clumpy growth of big bluestem allows room for other plants to exist and provides excellent habitat structure for nesting and roosting

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 40
Reviewed
Poison ivy is a vine that can grow up to 60 feet high or a low, upright shrub. It has alternate leaves with three oval to lance-shaped leaflets with a pointed tip.The flowers are greenish white and grow in clusters 1 to 4 inches long on new growth of stems.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 43
Reviewed
Common ragweed commonly grows to 18 inches. Leaves are simple, alternate, smooth and deeply lobed. Often the lobes are lobed again.