

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 45
Reviewed
Learn to identify and manage tobacco and tomato hornworms in your garden with tips on appearance, feeding habits, and control methods.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 16
Reviewed
European pine sawfly caterpillars (Neodiprion sertifer) are present in spring and summer. They produce one generation per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 48
Reviewed
Variegated cutworm caterpillars (Peridroma saucia) are present from late spring to early summer. They produce two to four generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 19
Reviewed
Gray furcula caterpillars (Furcula cinerea) are present from spring to fall. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 51
Reviewed
Red phase and black phase walnut caterpillars (Datana integerrima) are present from early May to September. They produce one to two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 54
Reviewed
Yellow woollybear caterpillars (Spilosoma virginica) are present from spring to fall. They produce two to three generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 22
Reviewed
Hackberry emperor caterpillars (Asterocampa celtis) are present from early summer to fall. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 25
Reviewed
Imperial moth caterpillars (Eacles imperialis) are present from June to August. They produce two generations per year. Common host plants include oaks, sweetgum, maple, hickory, sassafras, elm and sycamore.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 28
Reviewed
Linden looper caterpillars (Erannis tiliaria) are present from late spring to summer. They produce one generation per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 31
Reviewed
Pale tussock moth caterpillars (Halysidota tessellaris) are present from early summer to fall. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 02
Reviewed
Achemon sphinx caterpillars (Eumorpha achemon) are present from early summer to fall. They produce one to two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 34
Reviewed
Polyphemus moth caterpillars (Antheraea polyphemus) are present from May to October. They produce multiple generations per year.
Least-Toxic Control Methods to Manage Indoor Plant Pests
Reviewed
Learn safe and effective ways to manage indoor plant pests using natural, mechanical, and low-toxicity treatments that protect both plants and the environment

Reducing Losses When Feeding Hay to Beef Cattle
Reviewed
Feeding hay to cattle is expensive, mostly due to waste. Learn good management practices to minimize the losses that occur due to poor storage methods, improper feeding methods, or both.
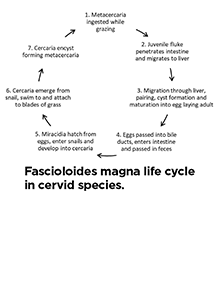
Liver Flukes in Missouri: Distribution, Impact on Cattle, Control and Treatment
Reviewed
Cattle operations should evaluate their risk for is Fascioloides magna, also known as the deer fluke or the giant liver fluke. Learn about its distribution in Missouri, its life cycle, treatment and more in this guide.

Pelvic Measurements and Calving Difficulty
Reviewed
Learn how pelvic measurements can help estimate calf birth weight and reduce calving difficulty in beef cattle.

Enlist Label Compliance: How to Determine Hydrologic Soil Groups
New
Learn how to use the USDA Web Soil Survey interactive map to determine your field's hydrologic soil group for the soil series on which you plan to apply an Enlist herbicide.
Decision-Making Techniques for Community Groups
Reviewed
Explore four decision-making techniques to help community groups identify and prioritize projects effectively.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 41
Reviewed
Pokeweed leaves are smooth, oblong and usually 6 to 8 inches in length, though they may grow up to 12 inches. Stems turn bright purple as the plant matures. Clusters of succulent, shiny purple berries, about 1/4 inch in diameter, occur at the tops of the plants.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 09
Reviewed
Several briar species grow tall canes that form large thickets of dense, prickly cover. The briars exhibit numerous five-petaled white flowers from April through June.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 44
Reviewed
Roundhead lespedeza is a tall perennial plant with reddish-brown seed heads and large leaves. It provides crucial food for bobwhite quail, especially in winter.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 12
Reviewed
Croton produces abundant seeds and is a common summer weed in pastures and other disturbed areas. A dense covering of white hairs gives croton flowers a fuzzy white appearance.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 47
Reviewed
Sideoats grama has fine leaves and widely spaced fine hairs along the leaf edge, especially near the collar. Most sideoats plants are 18-24 inches tall at maturity. It has a unique, oatlike seed that droops slightly off one side of the stalk.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 15
Reviewed
Common elderberry is a shrub that grows to 8 feet tall and forms dense colonies from root sprouts. The tops are multibranched, bearing opposite, pinnately compound leaves 4 to 12 inches long. Lance-shaped leaflets are 2 to 6 inches long, 1 to 2 inches wide and sharply toothed.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest
Reviewed
Learn how to identify plants important to bobwhites in the Midwest so that you can critically evaluate the food and cover components of habitat on your land.