

Controlling Voles in Horticulture Plantings and Orchards in Missouri - Page 2
Reviewed
Pine voles spend most of their lives under the ground in burrow systems. They can be found in forested areas but also inhabit fields next to woodlands. They feed on plant roots, flower bulbs, and the growing tissue (cambium) of tree roots.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 14
Reviewed
Eastern red cedar is a small to medium-sized tree up to 50 feet tall. It is an aromatic evergreen with a dense pyramid-shaped to cylindrical crown.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 49
Reviewed
Annual smartweeds has abundant, swollen nodes where the leaf meets the stem. Leaves are simple, alternate and parallel-veined; most are lanceolate. Flower clusters are white or pink, and at maturity the plant yields large numbers of seeds.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 17
Reviewed
Flowering spurge may reach 3 feet tall on richer soils. Inflorescences are multibranched, with multiple flower heads per branch. Flowers have five white petals with a yellow center and average about one-third inch across.

Managing for White-tailed Deer in Missouri: Setting and Accomplishing Management Goals
Reviewed
White-tailed deer management
This deer conservation guide is one in a series developed jointly by MU Extension and the Missouri Department of Conservation.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 52
Reviewed
Switch grass exhibits an upright, bunchy growth form. The leaves twist in a corkscrew-like pattern from the base to the tip of the blade.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 20
Reviewed
Goat’s rue, a member of the bean family, is readily identified by its striking flower, which consists of a cream-colored upper petal above two bright pink lower petals. Leaves are alternate, compound and usually hairy, with a pointed, hairlike tip.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 55
Reviewed
Trailing lespedezas are small, native lespedezas with trailing stems that can readily form thick mats over bare areas if left undisturbed. The small flowers range from purple to white and can produce a large quantity of seeds.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 23
Reviewed
Hairy lespedeza leaflets occur in threes. This perennial plant earns its name from its stem and oblong leaflets, both of which are covered with hairs.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 58
Reviewed
Leaves of Geranium species are deeply cleft and palmately lobed. Seeds are located within the sharply pointed “crane’s bill” formed by the tubelike style of the flower.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 26
Reviewed
Illinois bundleflower can be identified in summer by the doubly compound, fernlike leaves and white spherical flower heads. By fall, the stems become tough and woody, and the seedpods are distinctive, bearing a ball-shaped cluster of pods, each containing several flat, brown seeds.
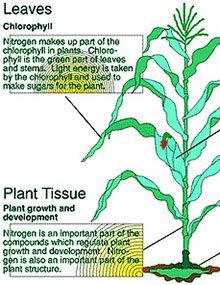
Nitrogen in the Plant
Reviewed
Nitrogen plays an important part in many essential functions. Visit our website to learn about Nitrogen in the Plant.
Fertilizer Nutrients in Dairy Manure
Reviewed
Discover effective strategies for managing dairy manure to optimize nutrient recovery and enhance crop productivity through proper manure handling.

Soybean Rust, Page 4
Revised
Frogeye leaf spot causes small, circular lesions on soybean leaves. It thrives in warm, humid conditions and survives in infected residue and seed.
Benefits and Risks of Biosolids
Reviewed
Biosolids are domestic wastewater sludge that meet standards for beneficial use as fertilizer. Visit our site to learn the Benefits and Risks of Biosolids.

Soybean Rust, Page 7
Revised
These photos show the disease stages of soybean rust, which can be difficult to identify, especially in the early stages.
Nitrogen in the Environment: Essential Plant Nutrients
Reviewed
Nitrogen is essential for plant growth, but excessive nitrate from fertilizers can contaminate groundwater, posing health risks, especially to infants.

Soybean Rust, Page 2
Revised
Identify and manage bacterial pustule in soybeans with guidance on symptoms, weather conditions, and disease development to protect your crops.

Soybean Rust, Page 5
Revised
Identify and manage Septoria brown spot in soybeans with insights on symptoms, weather impact, and control strategies. Learn how to protect your crop.

Soybean Rust, Page 8
Revised
Compare soybean rust disease stages by looking at them side by side.

Management of Grain Sorghum Diseases in Missouri
Reviewed
Manage grain sorghum diseases by planting resistant varieties, using quality seed, maintaining proper soil conditions, and implementing crop rotation.
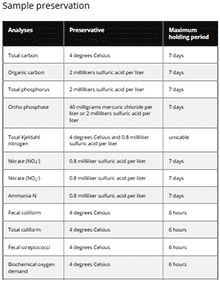
Collecting and Preserving Waste and Wastewater Samples for Analysis
Reviewed
Waste handling systems are used to protect the environment. Visit our site for our Collecting and Preserving Waste and Wastewater Samples for Analysis guide.

Soybean Rust
Reviewed
Learn the symptoms, development, and management strategies for soybean rust, a destructive disease caused by fungal pathogens that affects soybean crops.