

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 42
Reviewed
Possum haw grows mostly as a shrub but sometimes as a tree up to 30 feet tall. The twigs are slender with short, spurlike lateral twigs. The white flowers bloom in mid-spring either singularly or in clusters. Fruits are orange to red and globe-shaped.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 10
Reviewed
Broomsedge is a native warm-season grass that is often confused with little bluestem, but broomsedge stems are the more flattened and more densely leafed. Also, broomsedge in the fall/winter is typically yellowish tan, while little bluestem has a bronzy color.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 45
Reviewed
Sassafras provides essential cover and food for wildlife, offering berries for birds and fragrant leaves for deer and rabbits. It thrives in diverse habitats.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 13
Reviewed
Shrub dogwoods are common in fence lines and along forest edges. Individual plants are rather short (less than 12 feet tall) and somewhat rounded.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 16
Reviewed
False indigo occurs in moist ground in thickets along streams, rocky banks, pond borders and open wet woods. The leaves are pinnately compound. The dense flower clusters are deep purple to blue and produce numerous fruits that mature in late summer.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 48
Reviewed
Slender lespedeza leaves are divided into three leaflets 1 to 1-1/2 inches long and less than 1/4 inch wide. Stems are upright, up to 3 feet tall. Flowers are pink to purple and occur in clusters toward the top of the plant.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 19
Reviewed
Giant ragweed attains a considerable height, often in excess of 7 feet. Its leaves are three-lobed (sometimes five-lobed), and its stems may be 3/4 inch or more in diameter at the plant base.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 51
Reviewed
Sunflowers exhibit a variety of characteristics, but most of the commonly encountered species have triangular to lanceolate leaves, rough leaf surfaces and conspicuous yellow flowers.

Controlling Voles in Horticulture Plantings and Orchards in Missouri - Page 3
Reviewed
Meadow voles and prairie voles spend most of their lives above ground, living in and feeding on grasses and seeds. They may travel as far as 1/4 mile in search of food and cover. Their typical habitat includes lightly grazed pastures, old fields and grassy areas, lawns and gardens.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 22
Reviewed
Greenbriers grow as stout vines, climbing with the aid of tendrils that arise in pairs at the base of leaf stalks. The flowers are small and green and grow in clusters of 5 to 26 flowers on long stalks.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 54
Reviewed
Timothy is a cool-season bunch grass. By late spring it can be readily identified by the blue-green, cylindrical seed head resembling a small cattail. It has an elongated ligule at the base of the leaf, with a notch on each side.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 25
Reviewed
Huckleberries are stiffly branched leafy shrubs or small trees, often found in extensive colonies, from 6 inches to 10 feet tall. The alternate, simple leaves are 3/4 to 3 inches long and 1/2 to 1 inch wide. The fruits are blue to black berries with a faint whitish coating.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 57
Reviewed
Three species of wild bean occur in the Midwest. Each is a somewhat small plant with twining vines and relatively small leaves composed of three leaflets. Seeds are present in hairy pods.

Clear Writing
Reviewed
Get your point across clearly in writing with these 10 principles of clear writing. Also, learn how to test the clearness of your writing and keep it simple.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 28
Reviewed
Jewelweed commonly reaches 18-24 inches. Leaves have scalloped edges and fleshy stems that exude a clear, watery gel-like liquid when crushed. Flowers are orange (I. capensis) or pale yellow (I. pallida).

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 31
Reviewed
Little bluestem is a native grass that occurs in clumps with fine leaves less than 1/4 inch wide. Seed stalks are commonly 2 to 3 feet tall. Stems are hairy and flattened near the base. Seeds are light and fluffy.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 34
Reviewed
Orchard grass is a cool-season bunch grass. Its leaves have a bluish cast. Close inspection of the leaf collar reveals a flattened shape and membranous ligule. Its rather distinctive seed heads form by late May. Height at maturity averages 3 feet.
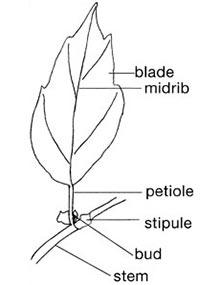
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 02
Reviewed
Refer to this glossary for definitions of words and phrases related to plants.
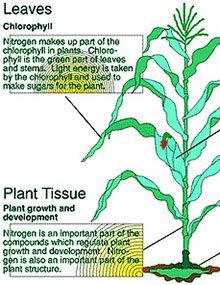
Nitrogen in the Plant
Reviewed
Nitrogen plays an important part in many essential functions. Visit our website to learn about Nitrogen in the Plant.

Management of Grain Sorghum Diseases in Missouri
Reviewed
Manage grain sorghum diseases by planting resistant varieties, using quality seed, maintaining proper soil conditions, and implementing crop rotation.
Fertilizer Nutrients in Dairy Manure
Reviewed
Discover effective strategies for managing dairy manure to optimize nutrient recovery and enhance crop productivity through proper manure handling.

Soybean Rust, Page 3
Revised
Pale yellow spots on young soybean leaves may signal downy mildew, favored by humid weather and temperatures between 68–72°F.

Soybean Rust, Page 6
Revised
Soybean rust causes lesions on leaves, spreads via windborne spores, and thrives in humid conditions between 46–82°F. It can rapidly defoliate plants.
Benefits and Risks of Biosolids
Reviewed
Biosolids are domestic wastewater sludge that meet standards for beneficial use as fertilizer. Visit our site to learn the Benefits and Risks of Biosolids.
Nitrogen in the Environment: Nitrification
Reviewed
Nitrification converts ammonium to nitrate, which can leach into groundwater, posing health risks, especially for infants.