

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 13
Reviewed
Shrub dogwoods are common in fence lines and along forest edges. Individual plants are rather short (less than 12 feet tall) and somewhat rounded.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 48
Reviewed
Slender lespedeza leaves are divided into three leaflets 1 to 1-1/2 inches long and less than 1/4 inch wide. Stems are upright, up to 3 feet tall. Flowers are pink to purple and occur in clusters toward the top of the plant.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 16
Reviewed
False indigo occurs in moist ground in thickets along streams, rocky banks, pond borders and open wet woods. The leaves are pinnately compound. The dense flower clusters are deep purple to blue and produce numerous fruits that mature in late summer.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 51
Reviewed
Sunflowers exhibit a variety of characteristics, but most of the commonly encountered species have triangular to lanceolate leaves, rough leaf surfaces and conspicuous yellow flowers.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 19
Reviewed
Giant ragweed attains a considerable height, often in excess of 7 feet. Its leaves are three-lobed (sometimes five-lobed), and its stems may be 3/4 inch or more in diameter at the plant base.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 22
Reviewed
Greenbriers grow as stout vines, climbing with the aid of tendrils that arise in pairs at the base of leaf stalks. The flowers are small and green and grow in clusters of 5 to 26 flowers on long stalks.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 54
Reviewed
Timothy is a cool-season bunch grass. By late spring it can be readily identified by the blue-green, cylindrical seed head resembling a small cattail. It has an elongated ligule at the base of the leaf, with a notch on each side.

Controlling Voles in Horticulture Plantings and Orchards in Missouri - Page 3
Reviewed
Meadow voles and prairie voles spend most of their lives above ground, living in and feeding on grasses and seeds. They may travel as far as 1/4 mile in search of food and cover. Their typical habitat includes lightly grazed pastures, old fields and grassy areas, lawns and gardens.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 25
Reviewed
Huckleberries are stiffly branched leafy shrubs or small trees, often found in extensive colonies, from 6 inches to 10 feet tall. The alternate, simple leaves are 3/4 to 3 inches long and 1/2 to 1 inch wide. The fruits are blue to black berries with a faint whitish coating.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 57
Reviewed
Three species of wild bean occur in the Midwest. Each is a somewhat small plant with twining vines and relatively small leaves composed of three leaflets. Seeds are present in hairy pods.

Clear Writing
Reviewed
Get your point across clearly in writing with these 10 principles of clear writing. Also, learn how to test the clearness of your writing and keep it simple.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 28
Reviewed
Jewelweed commonly reaches 18-24 inches. Leaves have scalloped edges and fleshy stems that exude a clear, watery gel-like liquid when crushed. Flowers are orange (I. capensis) or pale yellow (I. pallida).

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 31
Reviewed
Little bluestem is a native grass that occurs in clumps with fine leaves less than 1/4 inch wide. Seed stalks are commonly 2 to 3 feet tall. Stems are hairy and flattened near the base. Seeds are light and fluffy.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 34
Reviewed
Orchard grass is a cool-season bunch grass. Its leaves have a bluish cast. Close inspection of the leaf collar reveals a flattened shape and membranous ligule. Its rather distinctive seed heads form by late May. Height at maturity averages 3 feet.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 02
Reviewed
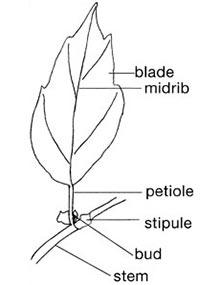
Refer to this glossary for definitions of words and phrases related to plants.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 37
Reviewed
Partridge pea grows from 12 to 18 inches up to 3 feet tall. It has compound, alternate leaves. Leaflets are less than 1 inch long. Flowers are bright yellow with reddish-purple bases, about 1 inch across. Ripened seedpods are red-brown.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 05
Reviewed
Barnyardgrass is most often found growing in moist areas. The large seeds of this grass make it an important food source for bobwhites.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 40
Reviewed
Poison ivy is a vine that can grow up to 60 feet high or a low, upright shrub. It has alternate leaves with three oval to lance-shaped leaflets with a pointed tip.The flowers are greenish white and grow in clusters 1 to 4 inches long on new growth of stems.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 08
Reviewed
Mature seed stalks of big bluestem are copper colored and often grow more than 5 feet tall. The clumpy growth of big bluestem allows room for other plants to exist and provides excellent habitat structure for nesting and roosting

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 43
Reviewed
Common ragweed commonly grows to 18 inches. Leaves are simple, alternate, smooth and deeply lobed. Often the lobes are lobed again.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 11
Reviewed
Often found in disturbed areas, crab grass tends to indicate early successional vegetation, and thus good quail habitat. However, late spring disturbance may result in a crab grass response heavy enough to displace other beneficial or desired plants.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 46
Reviewed
Sensitive brier has prostrate stems and seedpods covered with hooked barbs. Doubly compound, featherlike leaves close rapidly when touched or disturbed. Flower clusters are a fuchsia ball dotted with contrasting yellow stamens.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 14
Reviewed
Eastern red cedar is a small to medium-sized tree up to 50 feet tall. It is an aromatic evergreen with a dense pyramid-shaped to cylindrical crown.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 49
Reviewed
Annual smartweeds has abundant, swollen nodes where the leaf meets the stem. Leaves are simple, alternate and parallel-veined; most are lanceolate. Flower clusters are white or pink, and at maturity the plant yields large numbers of seeds.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 17
Reviewed
Flowering spurge may reach 3 feet tall on richer soils. Inflorescences are multibranched, with multiple flower heads per branch. Flowers have five white petals with a yellow center and average about one-third inch across.