

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Baked Tortilla Chips (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Quick and easy baked tortilla chips recipe using simple ingredients. Perfect for healthy snacks and fast meal prep.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Personal Snack Pizzas (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Cheesy Enchilada Stack (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Sauteed Kohlrabi (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Eat Good Feel Good - Pocket Folder (Bundle of 25)
New $47
This two-pocket folder includes the MyActivity Pyramid and MyPlate graphics. It also has information and suggestions for daily calorie and food intake.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Tropical Carrot, Pineapple and Raisin Salad (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Light Pumpkin Pie (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Black Bean Tacos (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Cabbage Comfort (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Toad in the Hole (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Simple, low-cost recipe featuring whole-wheat bread and egg, ready in 15 minutes. Includes nutrition info and food safety tips.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Cheesy Tex-Mex Bean Dip (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
A quick, nutritious recipe for a Cheesy Tex-Mex Bean Dip, featuring black beans, salsa, onion, cheese, and garlic powder.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Nutty Couscous with Raisins and Vegetables (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Quick and nutritious Nutty Couscous with Raisins and Vegetables combines wholesome ingredients for a simple, healthy meal.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Cheesy Italian-Style Vegetables (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Quick, healthy veggie recipe with squash, peppers, and cheese.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Crowd Pleasin’ Rice and Red Beans (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Mix and Go Snack Mix (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Homemade Sloppy Joes (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
This publication offers a quick and affordable homemade sloppy joe recipe, ideal for nutrition education and SNAP-Ed programs.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Quick and Easy Tuna Noodles (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Honey Glazed Carrots (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Summer Squash and Corn (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
This publication offers a collection of 25 quick, nutritious recipes featuring summer squash and corn, using simple ingredients and minimal preparation time.

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Smooth and Zesty Tomato Bisque (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Ranch Cottage Cheese Veggie Dip (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Pumpkin Bread (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Mixing-Vessel Composting System at a Large Swine Finishing Farm
New
Learn about the mixing-vessel composting system used on large swine farms to treat manure efficiently and improve soil quality.
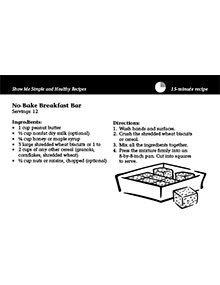
Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — No-Bake Breakfast Bar (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set

Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes — Pumpkin and Bean Soup (Bundle of 25)
Revised $10
Editor's note
The following abstract describes a publication that is available as a downloadable PDF. It is also available printed as part of the NC1 Show Me Simple and Healthy Recipes set