

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 25
Reviewed
Huckleberries are stiffly branched leafy shrubs or small trees, often found in extensive colonies, from 6 inches to 10 feet tall. The alternate, simple leaves are 3/4 to 3 inches long and 1/2 to 1 inch wide. The fruits are blue to black berries with a faint whitish coating.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 28
Reviewed
Jewelweed commonly reaches 18-24 inches. Leaves have scalloped edges and fleshy stems that exude a clear, watery gel-like liquid when crushed. Flowers are orange (I. capensis) or pale yellow (I. pallida).

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 31
Reviewed
Little bluestem is a native grass that occurs in clumps with fine leaves less than 1/4 inch wide. Seed stalks are commonly 2 to 3 feet tall. Stems are hairy and flattened near the base. Seeds are light and fluffy.
Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 02
Reviewed
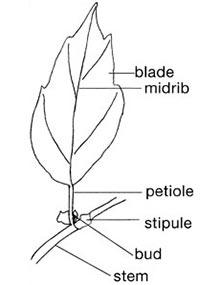
Refer to this glossary for definitions of words and phrases related to plants.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 34
Reviewed
Orchard grass is a cool-season bunch grass. Its leaves have a bluish cast. Close inspection of the leaf collar reveals a flattened shape and membranous ligule. Its rather distinctive seed heads form by late May. Height at maturity averages 3 feet.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 05
Reviewed
Barnyardgrass is most often found growing in moist areas. The large seeds of this grass make it an important food source for bobwhites.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 37
Reviewed
Partridge pea grows from 12 to 18 inches up to 3 feet tall. It has compound, alternate leaves. Leaflets are less than 1 inch long. Flowers are bright yellow with reddish-purple bases, about 1 inch across. Ripened seedpods are red-brown.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 08
Reviewed
Mature seed stalks of big bluestem are copper colored and often grow more than 5 feet tall. The clumpy growth of big bluestem allows room for other plants to exist and provides excellent habitat structure for nesting and roosting

Clear Writing
Reviewed
Get your point across clearly in writing with these 10 principles of clear writing. Also, learn how to test the clearness of your writing and keep it simple.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 40
Reviewed
Poison ivy is a vine that can grow up to 60 feet high or a low, upright shrub. It has alternate leaves with three oval to lance-shaped leaflets with a pointed tip.The flowers are greenish white and grow in clusters 1 to 4 inches long on new growth of stems.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 11
Reviewed
Often found in disturbed areas, crab grass tends to indicate early successional vegetation, and thus good quail habitat. However, late spring disturbance may result in a crab grass response heavy enough to displace other beneficial or desired plants.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 43
Reviewed
Common ragweed commonly grows to 18 inches. Leaves are simple, alternate, smooth and deeply lobed. Often the lobes are lobed again.

Controlling Voles in Horticulture Plantings and Orchards in Missouri - Page 2
Reviewed
Pine voles spend most of their lives under the ground in burrow systems. They can be found in forested areas but also inhabit fields next to woodlands. They feed on plant roots, flower bulbs, and the growing tissue (cambium) of tree roots.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 14
Reviewed
Eastern red cedar is a small to medium-sized tree up to 50 feet tall. It is an aromatic evergreen with a dense pyramid-shaped to cylindrical crown.

Techniques for Aging Live Deer
Reviewed
The ability to age live deer is a beneficial skill for all deer hunters and managers. Visit our site to learn Techniques for Aging Live Deer.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 46
Reviewed
Sensitive brier has prostrate stems and seedpods covered with hooked barbs. Doubly compound, featherlike leaves close rapidly when touched or disturbed. Flower clusters are a fuchsia ball dotted with contrasting yellow stamens.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 49
Reviewed
Annual smartweeds has abundant, swollen nodes where the leaf meets the stem. Leaves are simple, alternate and parallel-veined; most are lanceolate. Flower clusters are white or pink, and at maturity the plant yields large numbers of seeds.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 17
Reviewed
Flowering spurge may reach 3 feet tall on richer soils. Inflorescences are multibranched, with multiple flower heads per branch. Flowers have five white petals with a yellow center and average about one-third inch across.

Managing for White-tailed Deer in Missouri: Setting and Accomplishing Management Goals
Reviewed
White-tailed deer management
This deer conservation guide is one in a series developed jointly by MU Extension and the Missouri Department of Conservation.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 52
Reviewed
Switch grass exhibits an upright, bunchy growth form. The leaves twist in a corkscrew-like pattern from the base to the tip of the blade.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 20
Reviewed
Goat’s rue, a member of the bean family, is readily identified by its striking flower, which consists of a cream-colored upper petal above two bright pink lower petals. Leaves are alternate, compound and usually hairy, with a pointed, hairlike tip.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 55
Reviewed
Trailing lespedezas are small, native lespedezas with trailing stems that can readily form thick mats over bare areas if left undisturbed. The small flowers range from purple to white and can produce a large quantity of seeds.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 23
Reviewed
Hairy lespedeza leaflets occur in threes. This perennial plant earns its name from its stem and oblong leaflets, both of which are covered with hairs.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 58
Reviewed
Leaves of Geranium species are deeply cleft and palmately lobed. Seeds are located within the sharply pointed “crane’s bill” formed by the tubelike style of the flower.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 26
Reviewed
Illinois bundleflower can be identified in summer by the doubly compound, fernlike leaves and white spherical flower heads. By fall, the stems become tough and woody, and the seedpods are distinctive, bearing a ball-shaped cluster of pods, each containing several flat, brown seeds.