

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 43
Reviewed
Common ragweed commonly grows to 18 inches. Leaves are simple, alternate, smooth and deeply lobed. Often the lobes are lobed again.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 11
Reviewed
Often found in disturbed areas, crab grass tends to indicate early successional vegetation, and thus good quail habitat. However, late spring disturbance may result in a crab grass response heavy enough to displace other beneficial or desired plants.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 46
Reviewed
Sensitive brier has prostrate stems and seedpods covered with hooked barbs. Doubly compound, featherlike leaves close rapidly when touched or disturbed. Flower clusters are a fuchsia ball dotted with contrasting yellow stamens.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 14
Reviewed
Eastern red cedar is a small to medium-sized tree up to 50 feet tall. It is an aromatic evergreen with a dense pyramid-shaped to cylindrical crown.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 17
Reviewed
Flowering spurge may reach 3 feet tall on richer soils. Inflorescences are multibranched, with multiple flower heads per branch. Flowers have five white petals with a yellow center and average about one-third inch across.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 49
Reviewed
Annual smartweeds has abundant, swollen nodes where the leaf meets the stem. Leaves are simple, alternate and parallel-veined; most are lanceolate. Flower clusters are white or pink, and at maturity the plant yields large numbers of seeds.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 20
Reviewed
Goat’s rue, a member of the bean family, is readily identified by its striking flower, which consists of a cream-colored upper petal above two bright pink lower petals. Leaves are alternate, compound and usually hairy, with a pointed, hairlike tip.

Aging a Deer by Examining Its Jawbone
Reviewed
Managing the age structure of bucks is considered very important for improving the quality of the deer herd. Visit our site to learn about aging a deer.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 52
Reviewed
Switch grass exhibits an upright, bunchy growth form. The leaves twist in a corkscrew-like pattern from the base to the tip of the blade.
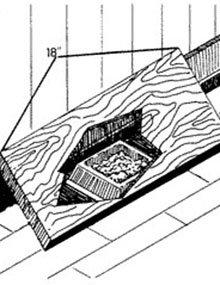
Bait Stations for Controlling Rats and Mice
Reviewed
Using bait stations to control rats and mice can be more effective and safe than using poison. Visit our website today to learn more.


Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 23
Reviewed
Hairy lespedeza leaflets occur in threes. This perennial plant earns its name from its stem and oblong leaflets, both of which are covered with hairs.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 55
Reviewed
Trailing lespedezas are small, native lespedezas with trailing stems that can readily form thick mats over bare areas if left undisturbed. The small flowers range from purple to white and can produce a large quantity of seeds.

Clear Writing
Reviewed
Get your point across clearly in writing with these 10 principles of clear writing. Also, learn how to test the clearness of your writing and keep it simple.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 26
Reviewed
Illinois bundleflower can be identified in summer by the doubly compound, fernlike leaves and white spherical flower heads. By fall, the stems become tough and woody, and the seedpods are distinctive, bearing a ball-shaped cluster of pods, each containing several flat, brown seeds.

Managing for White-tailed Deer in Missouri: Establishing a Wildlife Management Cooperative
Reviewed
Establishing a wildlife management cooperative enables landowners to collaboratively enhance white-tailed deer habitats and improve hunting opportunities.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 58
Reviewed
Leaves of Geranium species are deeply cleft and palmately lobed. Seeds are located within the sharply pointed “crane’s bill” formed by the tubelike style of the flower.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 29
Reviewed
Lambsquarters is rather nondescript and typically grows 2-6 feet tall. Leaves are triangular or kite-shaped, and their surfaces often have a powdery white appearance.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 32
Reviewed
Milkpea is a herbaceous legume with a hairy surface on the top of its trilobed leaf. Stems are also hairy. Seedpods are about 2-1/2 inches long.

Controlling Voles in Horticulture Plantings and Orchards in Missouri
Reviewed
Learn to manage vole damage in Missouri's horticultural plantings and orchards with effective control strategies for these small mammals.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 35
Reviewed
Osage orange grows as a medium-sized tree up to 50 feet tall. It has yellow-green fleshy fruits with a knobby surface that resembles a brain. Its alternate, simple leaves taper to a long, pointed tip.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 03
Reviewed
Alfalfa leaves are divided into three leaflets, with the middle leaflet on a distinct stalk. Leaflets are serrated along the outer third to half and are somewhat elongated. Flowers are usually purple, sometimes bluish, rarely white. Fruits are usually curved or twisted.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 38
Reviewed
Paspalums seeds are round and flattened and are neatly lined up (but sometimes overlapping slightly) on the seed stalk in two or four rows. Some paspalum species have conspicuous silky hairs at the base of the spikelet.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 06
Reviewed
Beggar's lice has triangular seedpods covered with dense hairs that cause them to stick to clothing. During the growing season, it can be recognized by its divided leaf and pink flower.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 41
Reviewed
Pokeweed leaves are smooth, oblong and usually 6 to 8 inches in length, though they may grow up to 12 inches. Stems turn bright purple as the plant matures. Clusters of succulent, shiny purple berries, about 1/4 inch in diameter, occur at the tops of the plants.