

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 27
Reviewed
Indian grass is a tall, warm-season nativethat averages 4 to 6 feet in height at maturity. Stems are stiff, and leaves are long and narrow. A characteristic of the plant is the notched ligule, suggesting the rear sight of a rifle.

Managing for White-tailed Deer in Missouri: Setting and Accomplishing Management Goals
Reviewed
This guide offers strategies to enhance deer habitat and manage populations effectively through goal setting and monitoring.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 59
Reviewed
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the following individuals and groups for their constructive review of this publication: Steve Clubine, Elsa Gallagher, Emily Horner, Lee Hughes, Aaron Jeffries, Matt Seek, Tim Smith, Bill White, and members of the Missouri Quail and Grassland Bird Technical Committee.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 30
Reviewed
Annual lespedeza and Korean lespedeza exhibit many similarities in growth form, occurring as semierect herbaceous plants with three-lobed leaves and reddish-purple to white flowers. Lower leaves are spreading while upper leaves stand erect.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 33
Reviewed
Oaks are long-lived trees that produce a seasonally important food for dozens of wildlife species. Their distinctive leaves and bark are identifying features.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 36
Reviewed
More than three dozen species of panic grass are commonly found across the Midwest. Seeds are football-shaped and borne on a sprawling, panicle-shaped seed head. The leaves of panic grasses resemble flags along the stem.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 04
Reviewed
American plum can grow as a small tree up to 20 feet high but more commonly occurs in colonies or thickets by sending up root suckers and shoots.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 39
Reviewed
Pigweed leaves are alternate and simple. Small green or tan flowers produce small, round, shiny black seeds. The roots are red when pulled. Depending on the species, pigweed may grow 1 to 8 feet tall.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 07
Reviewed
Bidens is most often found in moist areas. It has yellow flowers that are 1 to 1.5 inches.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 42
Reviewed
Possum haw grows mostly as a shrub but sometimes as a tree up to 30 feet tall. The twigs are slender with short, spurlike lateral twigs. The white flowers bloom in mid-spring either singularly or in clusters. Fruits are orange to red and globe-shaped.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 10
Reviewed
Broomsedge is a native warm-season grass that is often confused with little bluestem, but broomsedge stems are the more flattened and more densely leafed. Also, broomsedge in the fall/winter is typically yellowish tan, while little bluestem has a bronzy color.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 45
Reviewed
Sassafras provides essential cover and food for wildlife, offering berries for birds and fragrant leaves for deer and rabbits. It thrives in diverse habitats.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 13
Reviewed
Shrub dogwoods are common in fence lines and along forest edges. Individual plants are rather short (less than 12 feet tall) and somewhat rounded.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 16
Reviewed
False indigo occurs in moist ground in thickets along streams, rocky banks, pond borders and open wet woods. The leaves are pinnately compound. The dense flower clusters are deep purple to blue and produce numerous fruits that mature in late summer.

Quail-Friendly Plants of the Midwest, Page 48
Reviewed
Slender lespedeza leaves are divided into three leaflets 1 to 1-1/2 inches long and less than 1/4 inch wide. Stems are upright, up to 3 feet tall. Flowers are pink to purple and occur in clusters toward the top of the plant.
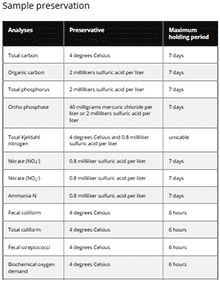
Collecting and Preserving Waste and Wastewater Samples for Analysis
Reviewed
Waste handling systems are used to protect the environment. Visit our site for our Collecting and Preserving Waste and Wastewater Samples for Analysis guide.

Soybean Rust, Page 4
Revised
Frogeye leaf spot causes small, circular lesions on soybean leaves. It thrives in warm, humid conditions and survives in infected residue and seed.

Soybean Rust
Reviewed
Learn the symptoms, development, and management strategies for soybean rust, a destructive disease caused by fungal pathogens that affects soybean crops.

Soybean Rust, Page 7
Revised
These photos show the disease stages of soybean rust, which can be difficult to identify, especially in the early stages.
Best Management Practices for Biosolids Land Application
Reviewed
Land application of biosolids recycles nutrients, reduces pollution, and follows safety practices to protect soil, crops, and water.
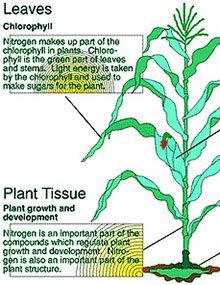
Nitrogen in the Plant
Reviewed
Nitrogen plays an important part in many essential functions. Visit our website to learn about Nitrogen in the Plant.
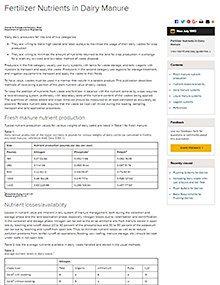
Fertilizer Nutrients in Dairy Manure
Reviewed
Discover effective strategies for managing dairy manure to optimize nutrient recovery and enhance crop productivity through proper manure handling.

Soybean Rust, Page 2
Revised
Identify and manage bacterial pustule in soybeans with guidance on symptoms, weather conditions, and disease development to protect your crops.

Soybean Rust, Page 5
Revised
Identify and manage Septoria brown spot in soybeans with insights on symptoms, weather impact, and control strategies. Learn how to protect your crop.

Soybean Rust, Page 8
Revised
Compare soybean rust disease stages by looking at them side by side.