
Spiders - Page 7
Reviewed
The publication provides detailed information about various spider species found in Missouri, including their biology, habits, and potential risks to humans.
Spiders
Reviewed
Spiders belong to the order Araneae of the class Arachnida. More than 300 different spiders occur in Missouri.

Spiders - Page 2
Reviewed
Learn to identify and manage common Missouri spiders, including black widow and brown recluse, with safety tips and control methods.
Spiders - Page 5
Reviewed
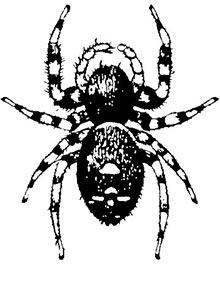
Jumping spiders are small, colorful arachnids that hunt during the day by stalking and pouncing on prey, using silk only as an anchor.
Spiders - Page 8
Reviewed
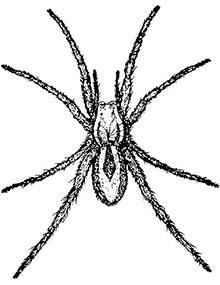
Wolf spiders are large, harmless hunters found in many habitats. Females carry egg sacs, and young ride on their backs after hatching.

All-Weather Concrete Stock Tank
Reviewed
Learn how to build an all-weather concrete stock tank, with measured and detailed plans.

Bats of Missouri: Information for Homeowners
Revised
Discover the diverse bat species in Missouri, their ecological benefits, and guidance on safely managing bat encounters in homes.

Soil Testing in Missouri
Reviewed
Find out how fertile your garden or lawn soil is with a soil test. Results estimate the ability of soil to supply plant nutrients or support plant growth. Learn the process of taking a soil sample and the tools necessary to do so in this guide.

Lawn and Garden Soil Test Interpretations and Fertilizer Recommendation Guide
Reviewed
Eliminate the guesswork of providing nutrients for plant growth and avoid potentially environmentally harmful fertilizer applications by having your home lawn and garden soil tested. Learn the methods used by the MU Soil and Plant Testing in this guide.

Alternative Crops in Double-Crop Systems for Missouri
Reviewed
Explore alternative crops like amaranth, buckwheat, pearl millet, and sunflower for double-cropping in Missouri to enhance profits and reduce pest cycles.
Transportation of Fish in Bags
Reviewed

Bluegill Sunfish Production in Missouri
Reviewed
Learn about bluegill sunfish aquaculture in Missouri, including species info, spawning, pond prep, and water quality management.

Freshwater Prawn Production in Missouri
Reviewed
Freshwater prawns (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) can be successfully and profitably produced in mid-Missouri. Learn about culture and management techniques that have been successful in producing freshwater prawns in this MU Extension guide.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 21
Reviewed
Greenstriped mapleworm caterpillars (Dryocampa rubicunda) are present from late spring to late fall. They produce one to two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 53
Reviewed
Whitemarked tussock moth caterpillars (Orgyia leucostigma) are present from May to October. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 24
Reviewed
Hickory horned devil caterpillars (Citheronia regalis) are present from July to October. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 56
Reviewed
Zebra swallowtail caterpillars (Graphium marcellus) are present from May to November. They produce two to three generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 27
Reviewed
Io moth caterpillars (Automeris io) are present from July to October. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 30
Reviewed
Orangedog caterpillars (Papilio cresphontes) are present from July to October. They produce two generations per year. They are considered a pest to citrus trees.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 33
Reviewed
Pickleworm caterpillars (Diaphania nitidalis) are present from summer to fall. They produce two to three generations per year.


Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 36
Reviewed
Red-spotted purple caterpillars (Limenitis arthemis) are present from early summer to fall. They produce two generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 04
Reviewed
Bagworm caterpillars (Thyridopteryx ephemeraeformis) are present from early June to August. They produce one generation per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 39
Reviewed
Smalleyed sphinx caterpillars (Paonias myops) are present from May through September. They produce multiple generations per year.

Caterpillars in Your Yard and Garden, Page 07
Reviewed
Cabbage looper caterpillars (Trichoplusia ni) are present from late spring to fall. They produce two to three generations per year.