

Growing Home Garden Tomatoes
Revised
Tomatoes are a popular home garden crop. They require little area, bear repeatedly, are easy to grow and have many culinary uses. Learn about various varieties and get tips for growing tomatoes in this guide.

Forcing Bulbs for Indoor Bloom
Reviewed
Forcing bulbs indoors brings spring color to your home during winter. Learn how to select, chill, and pot bulbs like daffodils, tulips, and hyacinths.

Growing Herbs at Home
Reviewed

Home Propagation of Houseplants
Reviewed
Plant pieces cut from a parent plant and rooted to form new plants are called “cuttings.” Use of cuttings is a simple, inexpensive way to multiply houseplants and garden plants.

Establishing and Managing Riparian Forest Buffers
Revised
Learn how to design and manage the interactive agroforestry practice of riparian forest buffers.

Growing Chinese Chestnuts in Missouri
Revised
Editor's note
This page currently contains only the introductory section of this guide. For the entire text, please download the PDF.
Lagoon Solids Removal and Solid Separation System Improvement at a Dairy Farm
Reviewed
Explore methods for managing lagoon solids in flush dairy systems, including removal techniques and solid separation system improvements.
5 Steps to Buying Meat Direct From the Farm
New
If you are interested in buying meat from a local farmer, in quarters or halves, review these five considerations: how much meat your family can consume and what cuts to buy, sourcing an animal, finding a local meat processor, costs, and timing.

Preserve It Fresh, Preserve It Safe: 2022, No. 3 (May/June)
New
Describes using sugar, syrup, or honey to preserve jams and canned fruit, plus reduced-sugar recipes and methods to dry or freeze strawberries.

Dairy Grazing: Heifer Development
Revised
Heifers are the foundation of any dairy enterprise and directly affect future profitability. Learn how to manage a heifer development program to maintain a herd with farm-raised heifers and save the cost of buying replacement heifers in this guide.

Creativity in Young Children
Reviewed
This guide explores how children express creativity and offers strategies for adults to nurture imaginative thinking.

All-Weather Concrete Stock Tank
Reviewed
Learn how to build an all-weather concrete stock tank, with measured and detailed plans.
Spiders - Page 3
Reviewed
Provides detailed information about the brown recluse spider, including its appearance, habitat, behavior, and medical implications of its bite.
Spiders - Page 6
Reviewed
Orb weavers, such as the yellow garden spider, are nonpoisonous and build large, sticky webs to catch insects like grasshoppers.
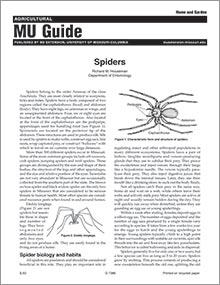
Spiders
Reviewed
Spiders belong to the order Araneae of the class Arachnida. More than 300 different spiders occur in Missouri.

Spiders - Page 4
Reviewed
Crab spiders (Thomisidae) are nonpoisonous ambush predators that capture prey by waiting motionless on flowers.
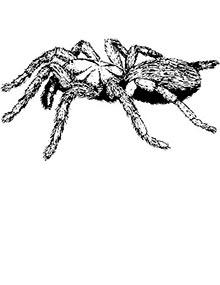
Spiders - Page 7
Reviewed
The publication provides detailed information about various spider species found in Missouri, including their biology, habits, and potential risks to humans.

Spiders - Page 2
Reviewed
Learn to identify and manage common Missouri spiders, including black widow and brown recluse, with safety tips and control methods.
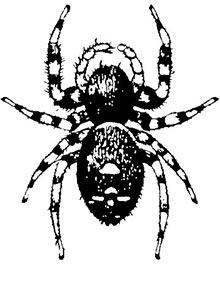
Spiders - Page 5
Reviewed
Jumping spiders are small, colorful arachnids that hunt during the day by stalking and pouncing on prey, using silk only as an anchor.
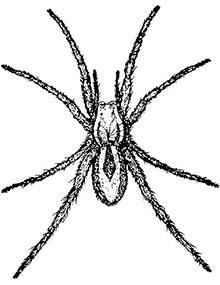
Spiders - Page 8
Reviewed
Wolf spiders are large, harmless hunters found in many habitats. Females carry egg sacs, and young ride on their backs after hatching.

Bats of Missouri: Information for Homeowners
Revised
Discover the diverse bat species in Missouri, their ecological benefits, and guidance on safely managing bat encounters in homes.

Soil Testing in Missouri
Reviewed
Find out how fertile your garden or lawn soil is with a soil test. Results estimate the ability of soil to supply plant nutrients or support plant growth. Learn the process of taking a soil sample and the tools necessary to do so in this guide.

Lawn and Garden Soil Test Interpretations and Fertilizer Recommendation Guide
Reviewed
Eliminate the guesswork of providing nutrients for plant growth and avoid potentially environmentally harmful fertilizer applications by having your home lawn and garden soil tested. Learn the methods used by the MU Soil and Plant Testing in this guide.

Alternative Crops in Double-Crop Systems for Missouri
Reviewed
Explore alternative crops like amaranth, buckwheat, pearl millet, and sunflower for double-cropping in Missouri to enhance profits and reduce pest cycles.
Transportation of Fish in Bags
Reviewed