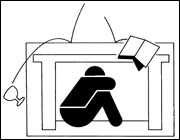
During the winter of 1811–1812, a legendary series of four earthquakes and hundreds to thousands of aftershocks struck southern Missouri near New Madrid. This series of disruptions is regarded as one of the largest seismic events in U.S. history. The greatest of the quakes measured approximately 7.4 on the Richter scale and was felt in the cities of Chicago, Washington, D.C., New Orleans and parts of Canada. The energy released from the earthquake was equal to 200 atomic bombs the size of those dropped on Hiroshima, or 20 million tons of TNT. Settlements in Missouri and Arkansas were devastated, the Mississippi River flowed north for several days. Boats capsized. An eyewitness to the New Madrid earthquake gave the following account: "The surface of the earth rose and fell like the long, low swell of the sea, tilting the trees until their branches interlocked, and opening the soil in deep cracks. Landslides swept down the steeper bluffs and hillsides. Large areas were uplifted, and still larger areas subsided and became covered with water emerging through fissures. High banks of the Mississippi caved in and became part of the river. Sand bars and points of islands gave way, and whole islands disappeared." Scientists estimate that an earthquake the magnitude of the 1811–1812 quakes will occur about every 670 years. Scientists largely agree that there is the potential for large earthquakes within or near to the New Madrid Seismic Zone.
Earthquake possible in Missouri
The New Madrid Seismic Zone (NMSZ) is the most active seismic area in the United States east of the Rocky Mountains. According to the Missouri Department of Natural Resources Division of Geologyand Land Survey, the NMSZ averages more than 200 measured events per year (magnitude 1 or greater), about 20 per month. Tremors large enough to be felt (magnitude 2.5 to 3.0) are measured annually. Every 18 months, a 4.0 or greater shock, capable of minor local damage, occurs. Events of 5.0 or greater occur about once every decade and can do significant damage and be felt in several states. If an event equal in magnitude to the largest 1811–1812 quake occurred today, it is estimated that the loss of life would be great and property damage would be many billions of dollars. There would be major damage near the fault system in the Missouri Bootheel, northeast Arkansas and western Kentucky and Tennessee. Significant damage is expected to extend north of St. Louis up the Mississippi River valley, up the Ohio and Wabash River valleys to near Owensboro, Kentucky, and Indiana, and down the Mississippi River valley to near Greenville, Miss. Significant damage is also expected in about 15 additional counties each in southern Illinois, western Kentucky and Tennessee, northeastern Arkansas and northwestern Mississippi and in about five counties in southeast Missouri outside the Bootheel.
Preparation lessens danger
This guide is designed to help you and your family plan for and survive a major earthquake. With advance preparation, the impact of an earthquake can definitely be lessened. Set aside some emergency supplies and plan with your family what to do at home during and after a disaster. You could be without help for up to 72 hours, so learn to cope for at least that long and possibly one week. Movement of the ground is seldom the actual cause of death or injury. Most injuries and casualties result from partial building collapses, falling objects and debris, such as toppling chimneys and falling bricks, ceiling plaster and light fixtures. Many of these conditions are preventable.
Because earthquakes occur without warning, it is important to take precautionary steps so you and your family can respond during this emergency.
Preparation saves lives
Before the earthquake happens, be prepared by having a home emergency supply kit available. The kit should include the following supplies:
- Flashlights with extra batteries
One of these flashlights should be near your bed. Never use matches or candles until you are certain no gas leak exists. - Portable radio with spare batteries
Most telephones will be out of order or should be used for emergency purposes only, so the radio will be your best source of information. - Well-stocked first aid kit and handbook
Every member of the family should have basic first aid knowledge and be competent in CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) - Fire extinguisher
Keep a multipurpose dry chemical extinguisher handy for small fires. Every family member should know where and how to use these fire extinguishers. - Food
Maintain a supply of nonperishable food that can be rotated into the family's diet and replaced on a regular basis. Have enough canned foods, a mechanical opener, powdered milk or canned juices for at least one week. Dried cereals, fruit and nonsalted nuts are a good source of emergency nutrition. - Water
Store water in airtight containers and replace about every six months. Store at least 6 gallons of water per person to be prepared for a one-week period. Have purification tablets such as Halazone and Globaline, but read the label on the bottle before using tablets.
Note
Water can be disinfected with 5.25 percent sodium hypochlorite solution (household chlorine bleach). Do not use a solution in which there are active ingredients other than hypochlorite. Use the following proportions:
| Quantity | Clean water | Cloudy water |
|---|---|---|
| Two liters | 4 drops | 1/8 teaspoon |
| One gallon | 1/8 teaspoon | 1/4 teaspoon |
| Five gallons | 1/2 teaspoon | 1 teaspoon |
- Special items
Have at least one week's supply of medications and special foods needed for infants or those on limited diets. - Tools
A pipe wrench and an adjustable wrench should be available for turning off gas and water mains. Family members should be taught where and how to shut off electricity, gas and water at the main, or main switch.
How to shut off gas
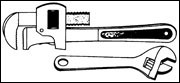
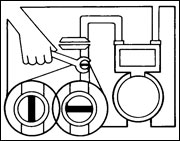
Your main gas shut-off valve is located next to your meter on the inlet pipe. On an LP gas system, the shut-off is located at the tank.
Use a wrench to give the valve a quarter turn in either direction so that the valve runs crosswise on the pipe. The gas line is now closed.
Caution
Do not shut off gas unless an emergency exists. If gas is ever turned off, remember that all pilot lights must be relit when the gas is turned back on.
How to shut off water
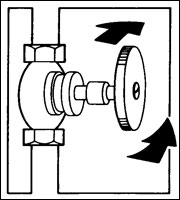
Locate the water shut-off valve where it enters the house. Show all family members where the valve is. Also locate the main water shut-off at the water meter.
How to shut off electricity
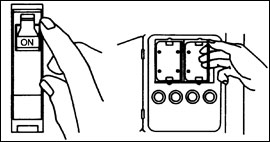
Look closely at your circuit breaker box or fuse box. Locate the main cartridge fuses or circuit breaker.
Be certain you can shut off electricity if there is damage to your home electrical wiring. To properly shut down the electrical circuits in your home, turn off each breaker one at a time and then shut off the main breaker. Reverse these steps to re-energize the home's electrical panel.
Staying calm is very important
First and foremost — keep calm. During a major earthquake, you may experience a shaking that starts out to be gentle and within a second or two grows violent and knocks you off your feet. Or, you may be jarred by a violent jolt — as though your house is being hit by a truck. A second or two later you will experience the shaking, making it difficult (if not impossible) to move from one room to another.
If you are indoors, stay there. Take cover under a heavy desk, table or bench, in a supported doorway, or along an inside wall. Stay away from windows, bookcases, china cabinets, mirrors and fireplaces until the shaking stops.
If you are in the kitchen, turn off the stove at the first sign of shaking and quickly take cover under a counter or sturdy table, or in a doorway.
If you are in a high-rise building, get under a desk or similar heavy furniture, and stay away from windows and outside walls. Stay in the building on the same floor. Do not dash for exits because stairways may be broken or jammed with people. Don't be surprised if the electricity goes off, or if fire alarm systems or sprinklers go on. Do not use elevators.
If you are in your car, pull to the side of the road and stop the car. Do not park under overpasses or power lines. Stay in your car until the earthquake is over. When you drive on, watch for hazards created by the earthquake, such as fallen or falling objects, downed electric wires, damaged, broken or undermined bridges, roadways or overpasses.
Check for injuries
- If anyone has stopped breathing, give mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, now called rescue breathing.
- Stop any bleeding injuries by applying direct pressure to the wound. For more detailed emergency procedures, consult your first aid book.
- Do not attempt to move seriously injured persons unless they are in immediate danger of future injury.
- Cover injured persons with blankets to keep them warm. Be reassuring and calm.
- Do not use the telephone unless there is a severe injury.
- Wear shoes in all areas near fallen debris and broken glass.
- Immediately clean up any spilled medicines, drugs or other potentially harmful materials — bleaches, lye, gasoline or other petroleum products.
Check for safety
- Check your home for fire or fire hazards. If possible, put out small fires. If not possible, leave your home immediately, alert your neighbors and call the fire department.
- Check utility lines and appliances for damage. If you smell gas or see a broken line, shut off the main valve. Do not search for a leak with a match or lighter. Do not use electrical switches or appliances, because sparks can ignite gas from leaks or broken lines. Do not switch on the gas or electricity until the utility company has checked your home.
- Do not touch downed power lines or objects touching downed lines or electrical wiring of any kind.
- Check to see that sewage lines are intact before using drains or toilets. Plug bathtub, shower, drain or sink drain to prevent sewage backup.
- Check your home, chimney and other structures for cracks and damage. Approach chimney and masonry walls with caution — they may topple. Do not use a fireplace or chimney unless it is undamaged and without cracks. When in doubt, don't use it.
- Check closets and cupboards. Open doors cautiously. Beware of falling objects tumbling off shelves.
Check your food supply
If water is off, emergency water supplies may be all around you — in water heaters, toilet water tanks, melted ice cubes, canned fruits and vegetables, etc.
Do not eat or drink anything from open containers near shattered glass. Liquids may be strained through a clean handkerchief, cloth or cheesecloth if danger of glass contamination exists.
If power is off, check your freezer and plan meals to use up foods that will spoil quickly. Keep your freezer door closed and insulate the freezer with blankets or quilts to reduce cooling loss. Cook thawed frozen foods immediately if they are still cool. If in doubt about their safety, do not use them.
Use outdoor charcoal broilers for emergency cooking. Never use the cookers indoors because of fire and carbon monoxide hazards.
If you must evacuate
- Don't use your vehicle unless there is an emergency. Don't go sightseeing. You will only hamper relief efforts. Keep streets and roads clear for the passage of emergency vehicles.
- Don't use your telephone except to report medical or fire emergencies or violent crimes.
- Turn on your portable radio for emergency information and damage reports.
- Be prepared for aftershocks. Most of these are weaker than the main quake, but some may be large enough to do additional damage.
- Cooperate with public safety officials, including fire fighters, police and medical personnel. Do not go into the damaged areas unless your help is requested.
- If you must evacuate your home — post a message in clear view where you can be found. Take medicine, first aid kit, flashlights, radio and batteries, important papers, and cash, food, sleeping bags or blankets and extra clothing with you to the emergency shelter. Don't forget to make arrangements for your pets. Have food, water, medications and cages ready for your evacuation. Don't leave them behind and assume you will be able to return to your home to care for them once you have evacuated.
The potential for earthquakes in Missouri always exists. Family earthquake preparedness and what family members do during and immediately after the tremor can help minimize damage and may make a life-or-death difference.
More information
Missouri Department of Natural Resources, Division of Geology and Land Survey
111 Fairgrounds Road
Rolla, Mo. 65402
573-368-2100
800-361-4827
Geologic Hazards